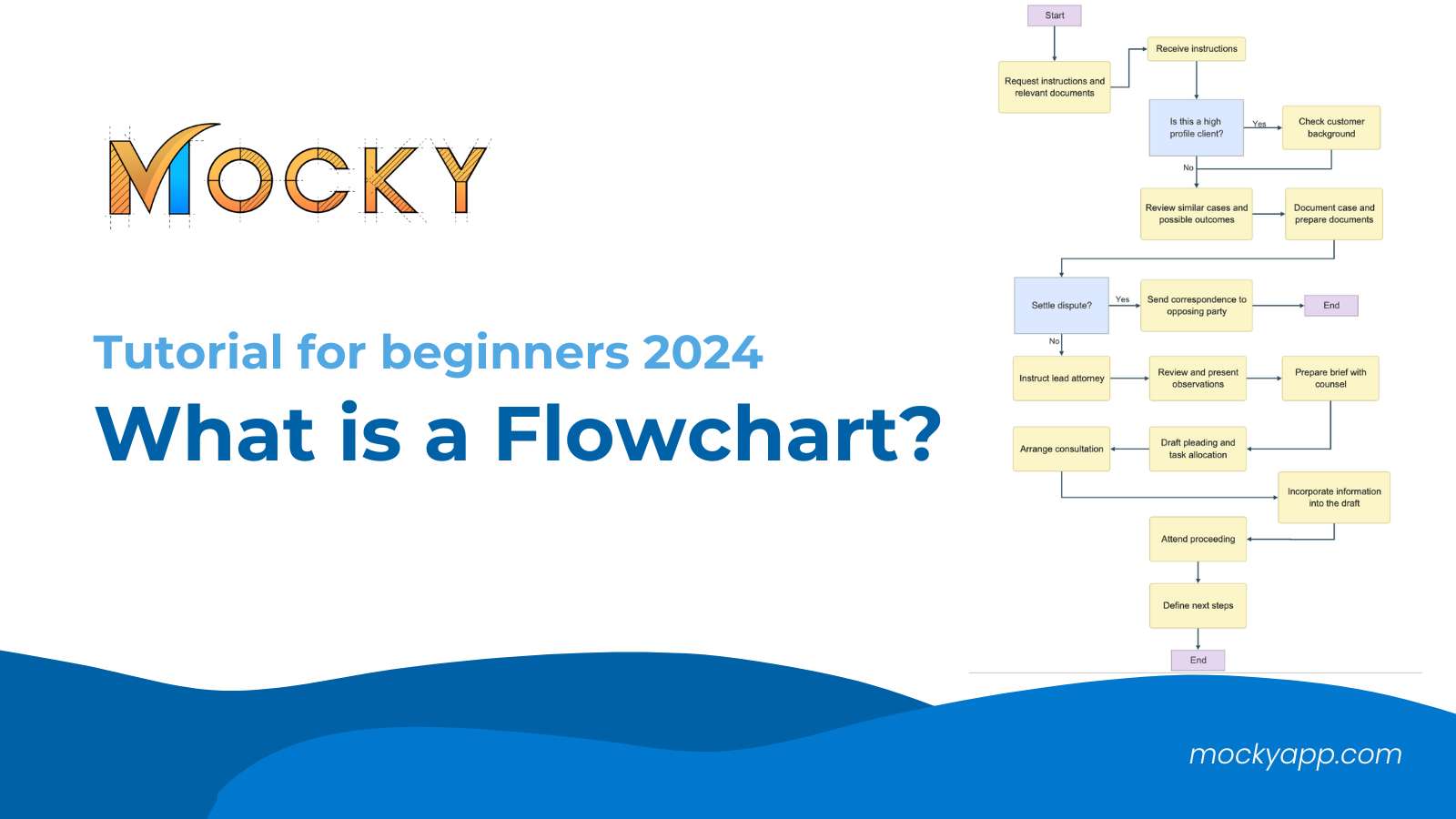
Table of Contents
- What is diagramming?
- The list of 20 purposes for diagramming
- 1. Improved communication
- 2. Increased efficiency
- 3. Better problem-solving
- 4. Better memory retention
- 5. Increased collaboration
- 6. Clarification of complex information
- 7. Identification of patterns and relationships
- 8. Representation of data
- 9. Establishing connections
- 10. Planning and design
- 11. Visualization of ideas
- 12. Understanding cause and effect
- 13. Documentation
- 14. Training and education
- 15. Improved decision-making
- 16. System analysis
- 17. Modeling
- 18. Prototyping
- 19. User experience design
- 20. Process improvement
- Conclusion on purposes of diagramming
What is diagramming?
Diagramming is a visual method of representing information, concepts, and relationships. It allows individuals to take complex information and present it in a simplified, visual format that is easy to understand. By using symbols, shapes, and lines to represent different components, the main purposes of diagramming are to clarify and communicate information in a way that is more intuitive and memorable than text-based information.
Additionally, diagrams can be used in a variety of fields and for a variety of purposes, including process flow diagrams, organizational charts, network diagrams, mind maps, and entity-relationship diagrams. Each type of diagram can represent different kinds of information and relationships, making it easier to understand complex information in a specific context.
For example, a flowchart is often for representing a series of steps in a process, making it easier to understand the flow of information and identify areas that need improvement.
An organizational chart, on the other hand, can help users represent the structure and relationships of individuals within a company or organization, helping to clarify the chain of command and communication channels.
The list of 20 purposes for diagramming
1. Improved communication
By visualizing information in a diagram, it can present such information in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for individuals to understand and retain. This is especially important when communicating complex ideas or information between individuals or teams who may have different backgrounds or areas of expertise.
2. Increased efficiency
By simplifying complex systems and processes, diagrams can help to identify areas of inefficiency and streamline processes. This can result in increased productivity and cost savings.
For example, people can use diagrams to represent a software development process, making it easier to identify areas where the process can be improved or streamlined.
3. Better problem-solving
Diagrams can help to identify and resolve problems by visually representing the relationships between different components and highlighting areas that need attention.
For example, a flowchart can help represent a business process, making it easier to identify areas causing bottlenecks or delays.
4. Better memory retention
The human brain processes visual information faster and retains it for a longer period of time than text-based information. By using diagrams to represent information, individuals can improve their memory retention of the information over time, making it easier to recall and apply the information later.
5. Increased collaboration
Diagrams provide a common visual language to facilitate communication and collaboration between team members. This can help to align goals, resolve conflicts, and increase overall collaboration.
For example, a team could use a flowchart to represent a project, making it easier to understand the interdependencies between different tasks and how they contribute to the overall project.
6. Clarification of complex information
One of the purposes of diagramming is to break down complex information into smaller, more manageable parts, making it easier to understand and remember.
For example, a diagram of a complex system, such as a computer network, can help to clarify the relationships between different components and make it easier to understand and manage the system.
7. Identification of patterns and relationships
Diagrams can help to identify patterns and relationships between different components that may not be immediately apparent, providing a clearer understanding of the information.
For example, a diagram of a financial system can help to identify relationships between different financial instruments and how they are impacted by different market conditions.
8. Representation of data
Diagrams help represent data in a visual format, making it easier to understand trends and patterns in the data. This can be useful in data analysis and decision-making.
For example, a bar chart can be used to represent data on sales over time, making it easier to understand trends and make informed decisions about future sales strategies.
9. Establishing connections
By visually representing the relationships between different components, diagrams can help to establish connections and understand the interdependence of different elements.
For example, a diagram of a supply chain can help to understand how different suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors are connected and how they impact each other.
10. Planning and design
Diagrams contribute to the planning and design stages of a project to help refine ideas and concepts, identify potential problems, and make informed decisions.
For example, a site plan diagram can play a role in representing a construction project. As a result, it is easier to understand the layout of the site and make informed decisions about the placement of different buildings and structures.
11. Visualization of ideas
Diagrams allow users to represent and visualize ideas, making it easier to communicate and understand them. This can be useful in brainstorming and idea generation.
For example, a mind map can be used to represent a collection of ideas, making it easier to organize and prioritize them.
12. Understanding cause and effect
By visually representing cause-and-effect relationships, diagrams can help individuals to understand how different components interact and the impact they have on each other. This can be useful in root-cause analysis and problem-solving.
13. Documentation
Diagrams can be document systems, processes, and data, providing a clear and concise representation of information for easy understanding and referring to later.
This is especially important in fields such as software development and engineering, where information needs to be captured and retained over time.
14. Training and education
Diagrams can represent information in a visual format, making it easier for individuals to understand and retain information, especially in a training or educational context.
For example, a diagram of a software application can help users understand how to use the application and the different features and functions it provides.
15. Improved decision-making
By visualizing information in a clear and concise manner, diagrams can help individuals to make informed decisions. This is especially important in situations where there is a lot of data to consider, as diagrams can help to simplify the information and make it easier to understand.
16. System analysis
Diagrams can also help analyze systems, including their strengths and weaknesses, to identify areas for improvement.
For example, a diagram of a software system can help to identify areas where the system is not performing optimally and identify ways to improve performance.
17. Modeling
Diagrams can be helpful in modeling complex systems, such as computer networks or financial systems. Besides, they help users understand how they work and identify areas for improvement.
This is especially important in fields such as software development and engineering, where accurate models of systems are critical to success.
18. Prototyping
Another purpose of diagrams is to create prototypes of software applications or other systems to help test and refine ideas. This is especially important in the software development process, where prototypes are used to evaluate and refine the user interface and functionality of an application.
19. User experience design
Diagrams can be used to design and refine the user experience of software applications, websites, and other systems. As a result, they help to ensure that the user experience is optimal and that the system is user-friendly and easy to use.
20. Process improvement
Diagrams focus on identifying and improving processes, including business processes and software development processes. This can help to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase overall performance.
For example, a flowchart can represent a business process, making it easier to identify areas where the process can be improved or streamlined.
Conclusion on purposes of diagramming
Diagramming is a powerful tool for a wide range of purposes, including system analysis, design, documentation, training and education, and process improvement. By visually representing information in a clear and concise manner, diagrams can help individuals to understand complex systems and make informed decisions.
Whether you’re working in software development, engineering, business, or another field, the ability to create and use diagrams is an important skill with a significant impact on your work and success.
Stay tuned with Mocky to keep yourself updated with diagram basics.